Warning: Undefined array key "file" in /home/www/wwwroot/HTML/www.exportstart.com/wp-content/themes/1198/header.php on line 7
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/www/wwwroot/HTML/www.exportstart.com/wp-content/themes/1198/header.php on line 7
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/www/wwwroot/HTML/www.exportstart.com/wp-content/themes/1198/header.php on line 7
- ʻApelika
- Alapania
- Amahapika
- Apapika
- Ameniana
- Azerbaijani
- Pōkē
- ʻŌlelo Belarusa
- Penekali
- Ponia
- Pukalia
- ʻŌlelo Katalonia
- Cebuano
- Kina
- Kina (Taiwan)
- ʻŌlelo Kokia
- Koalia
- Keka
- Kenemaka
- Hōlani
- Pelekania
- ʻŌlelo Esperanto
- Ekekonia
- Pinilana
- Palani
- Frisian
- Kalikia
- Keokia
- Alemania
- Helene
- Kuhalaki
- ʻŌlelo Haiki
- Hauka
- ʻŌlelo Hawaiʻi
- Hepela
- ʻAʻole
- Miao
- Hunakalia
- ʻĀinahau
- igbo
- ʻInikonia
- Ipelana
- Ikalia
- Kepanī
- Kawanī
- Kanākā
- ʻŌlelo Kazaka
- Khmer
- Rwandan
- Kolea
- ʻŌlelo Kurdish
- ʻŌlelo Kyrgyz
- TB
- ʻŌlelo Lākni
- Lakiwiana
- ʻŌlelo Lituania
- ʻŌlelo Lukemapuka
- Makekoni
- Malgashi
- Mālei
- Mālealama
- Malkī
- ʻŌlelo Māori
- Malapi
- ʻŌlelo Monokolia
- Maianamara
- Nepali
- Nolewai
- Nolewai
- ʻOkitana
- ʻŌlelo Pashto
- Pelekia
- Pōlani
- Pukikī
- ʻŌlelo Punajabi
- Lomānia
- Lukia
- Sāmoa
- Gaelika Sekotia
- ʻŌlelo Serbia
- Pelekania
- Shona
- Kiniki
- Sinhala
- Kolowakia
- Kolewenia
- ʻŌlelo Somalia
- Kepania
- ʻōlelo Sunda
- Kawahili
- Kuekene
- Kakalo
- Tajika
- Kamili
- Tatar
- Keluku
- Kailani
- Tureke
- ʻŌlelo Kuleke
- Ukrainian
- Urdu
- Uighur
- ʻUzbek
- Vietnamese
- Welsh
- Kokua
- Yiddish
- Yoruba
- Zulu
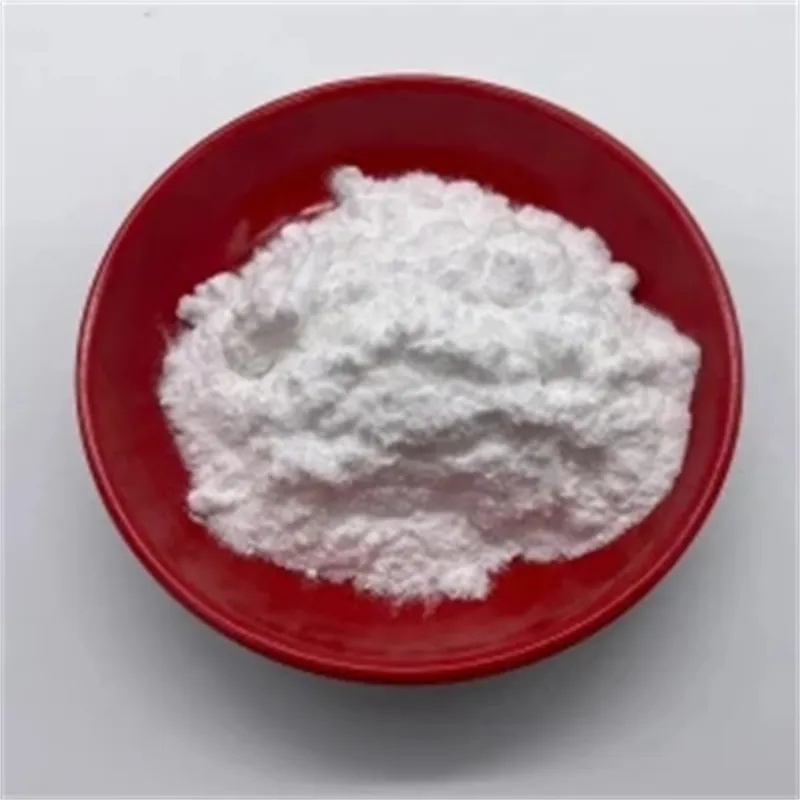
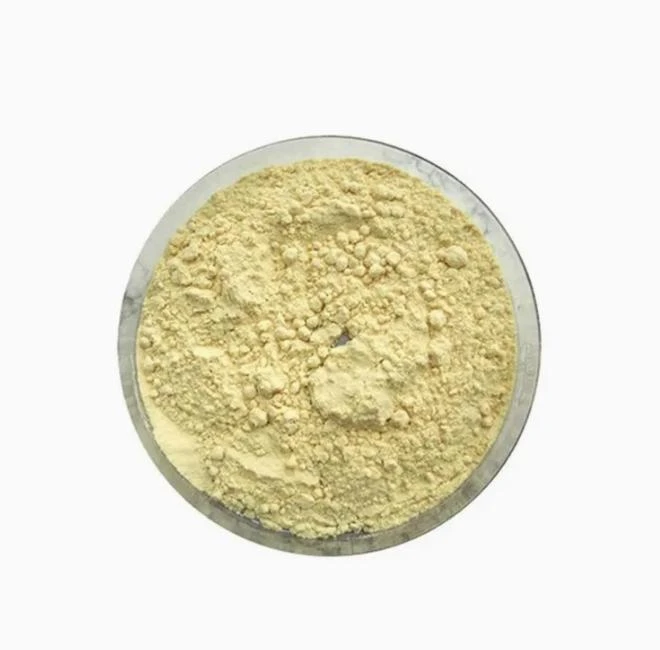
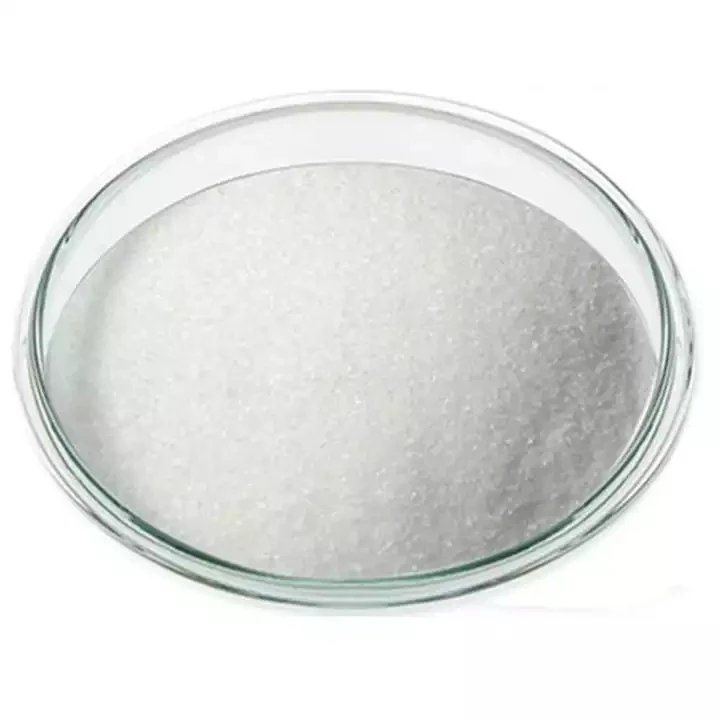
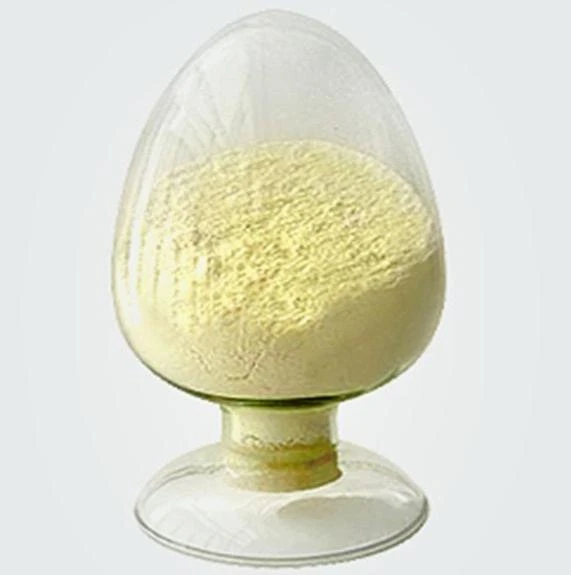
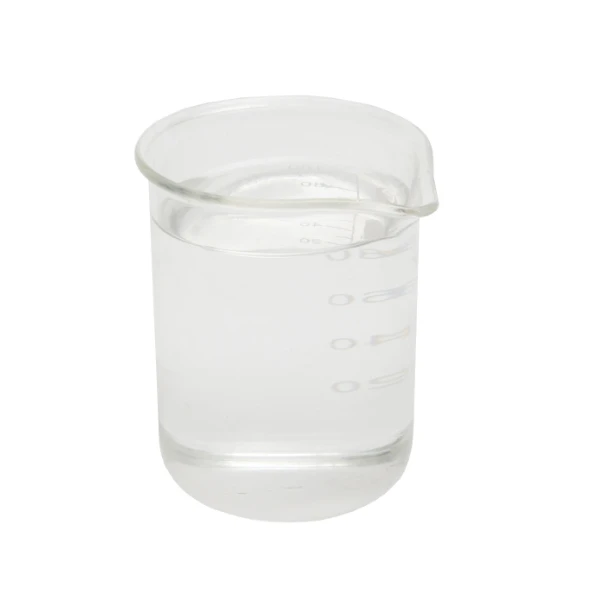
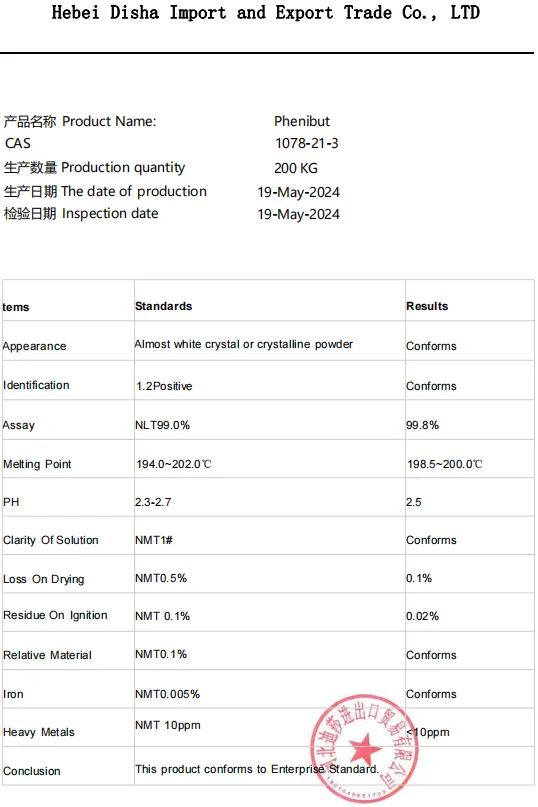
Phenibut
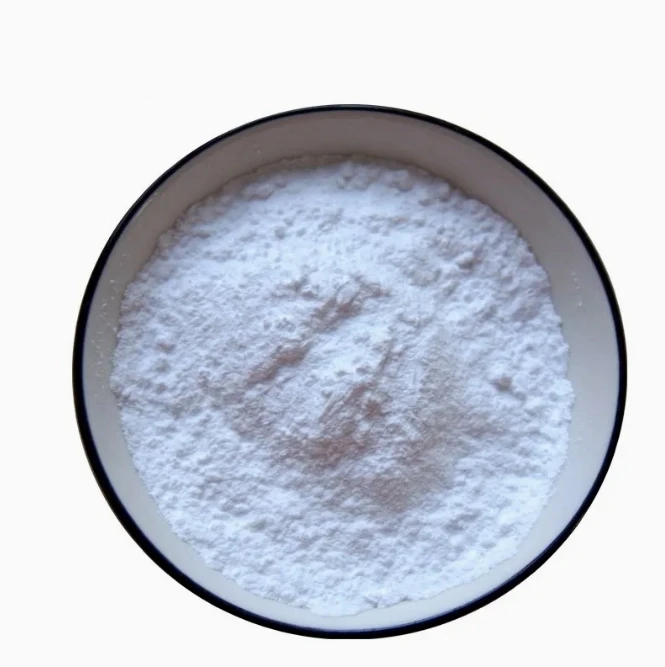
Phenibut (Aminophenylbutyric acid) is a central depressant and derivative of the naturally occurring inhibitory neurotransmitter γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA).
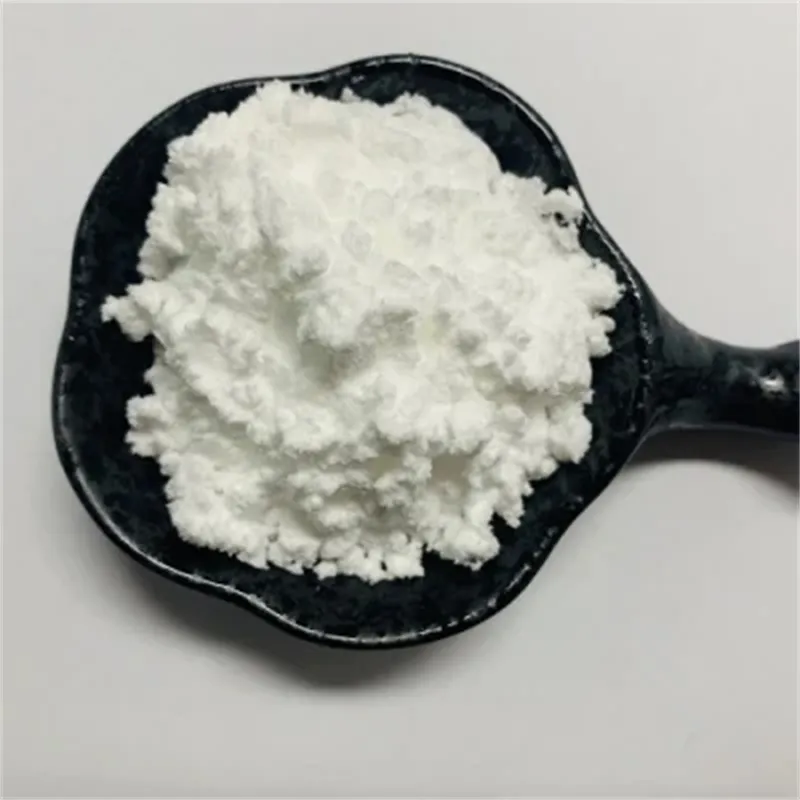
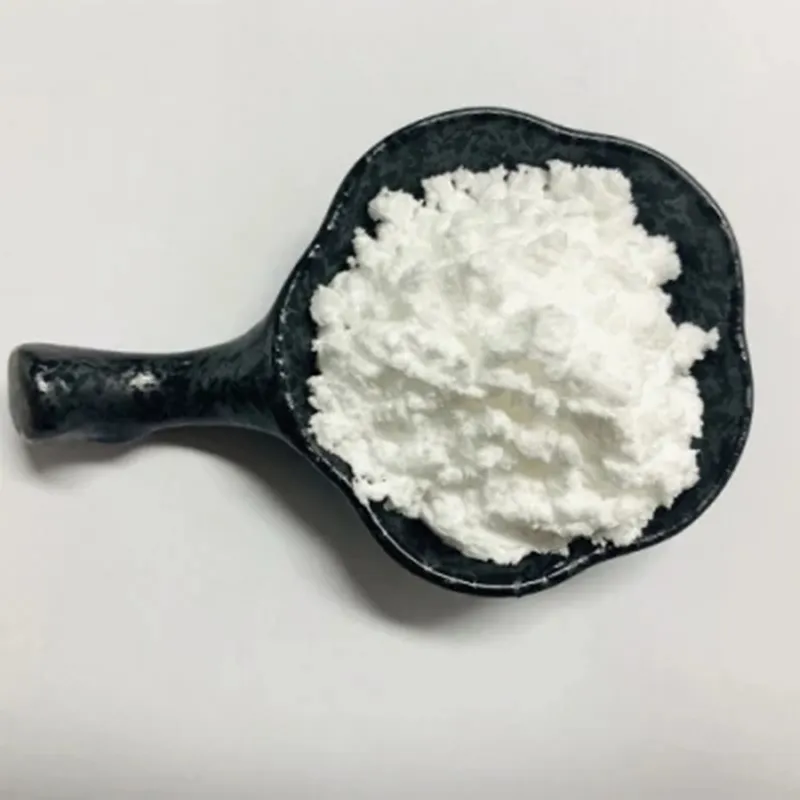
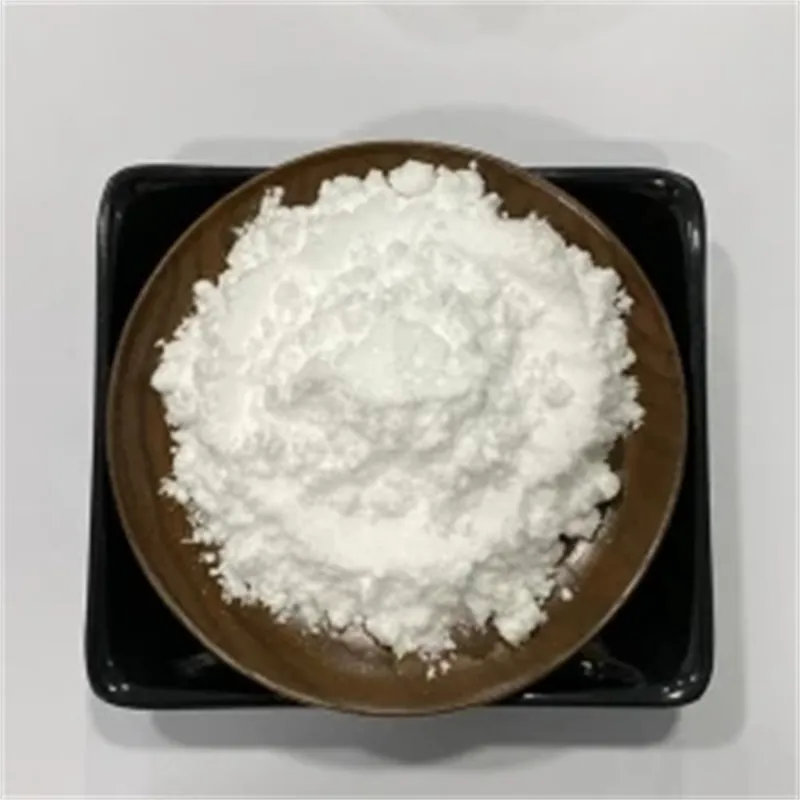
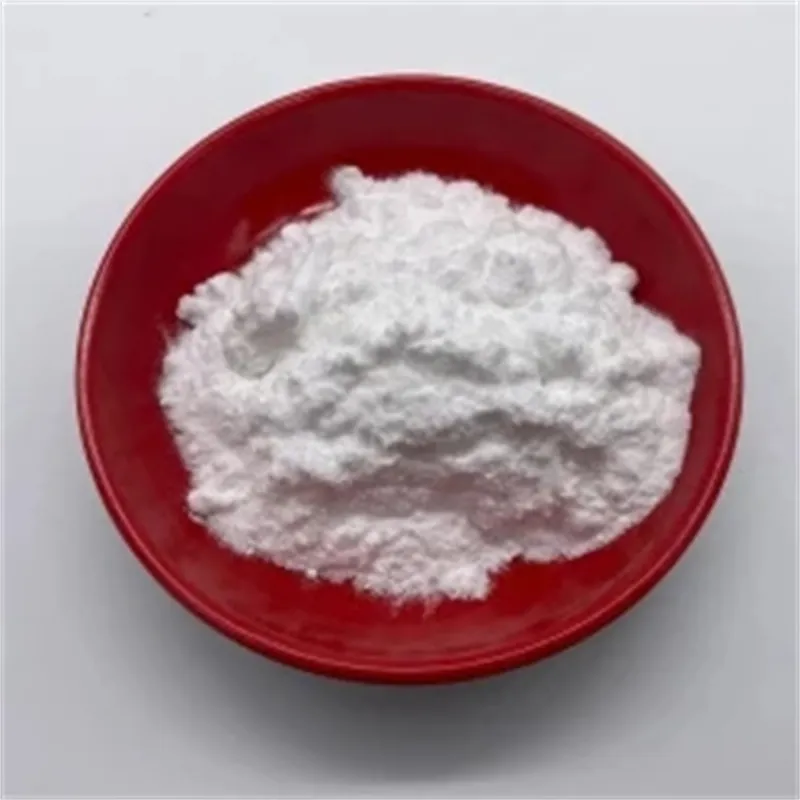




Phenibut (Aminophenylbutyric acid) is a GABA-B agonist, which can be used as GABA analogues, mainly acting on GABAB receptors, and has anti-anxiety and cognitive enhancement effects.
Phenibut is often used in the preparation of antidepressants and is a very important pharmaceutical intermediate that can be used in laboratory research and development processes and chemical pharmaceutical manufacturing processes.
Loaʻa iā mākou nā hale hana kiʻekiʻe me ka pilina hohonu, hiki iā ia ke hāʻawi iā ʻoe i nā huahana kiʻekiʻe a me nā kumukūʻai hoʻokūkū. A hiki iā mākou ke hāʻawi i nā uku no nā kūʻai nui. A ke hui pū nei mākou me nā ʻoihana lawe ukana ʻoihana he nui, hiki ke hāʻawi i nā huahana me ka palekana a me ka maʻalahi i kou mau lima. ʻO ka manawa hoʻouna ma kahi o 3-20 mau lā ma hope o ka hōʻoia ʻana o ka uku.




Biological activity
Phenibut (Aminophenylbutyricacid Fenibut, Phenigam Phenybut, PhGABA, beta PhChemicalbookenyl - gamma - aminobutyricacid, beta - Phenyl - GABA). As GABA analogues, it is a sedative that targets the central nervous system and has anti-anxiety and sedative effects.
Māhele huahana
-
 Apr . 27, 2025Zibo will host the 2025 International Chemical ExpoZibo, a city known for its thriving chemical industry, will host the 2025 Zibo International Chemical Expo from May 16 to May 18, 2025. This highly anticipated event aims to bring together industry leaders, innovators and stakeholders from around the world to explore the latest advancements and trends in the chemical industry.
Apr . 27, 2025Zibo will host the 2025 International Chemical ExpoZibo, a city known for its thriving chemical industry, will host the 2025 Zibo International Chemical Expo from May 16 to May 18, 2025. This highly anticipated event aims to bring together industry leaders, innovators and stakeholders from around the world to explore the latest advancements and trends in the chemical industry. -
 Apr . 22, 20252025 Yokohama Cosmetics Raw Materials and Technology ExhibitionYOKOHAMA, Japan – The City of Yokohama is preparing to host the much-anticipated Cosmetics Ingredients & Technologies 2025 from May 14 to May 16, 2025. The premier event is expected to attract industry professionals, innovators and enthusiasts from around the world to showcase the latest advancements in cosmetic ingredients and technologies.
Apr . 22, 20252025 Yokohama Cosmetics Raw Materials and Technology ExhibitionYOKOHAMA, Japan – The City of Yokohama is preparing to host the much-anticipated Cosmetics Ingredients & Technologies 2025 from May 14 to May 16, 2025. The premier event is expected to attract industry professionals, innovators and enthusiasts from around the world to showcase the latest advancements in cosmetic ingredients and technologies. -
 Apr . 18, 20252025 India Mumbai Fine Chemicals ExhibitionMUMBAI, India – The bustling metropolis of Mumbai is gearing up to host the much-anticipated Fine Chemicals Expo on April 29-30, 2025. The premier event is expected to attract industry leaders, innovators and stakeholders from across the world to showcase the latest advancements in the fine chemicals sector.
Apr . 18, 20252025 India Mumbai Fine Chemicals ExhibitionMUMBAI, India – The bustling metropolis of Mumbai is gearing up to host the much-anticipated Fine Chemicals Expo on April 29-30, 2025. The premier event is expected to attract industry leaders, innovators and stakeholders from across the world to showcase the latest advancements in the fine chemicals sector.













