Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/www/wwwroot/HTML/www.exportstart.com/wp-content/themes/1198/header.php on line 6
Warning: Undefined array key "file" in /home/www/wwwroot/HTML/www.exportstart.com/wp-content/themes/1198/header.php on line 7
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/www/wwwroot/HTML/www.exportstart.com/wp-content/themes/1198/header.php on line 7
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/www/wwwroot/HTML/www.exportstart.com/wp-content/themes/1198/header.php on line 7
- Afrikaans
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Arabic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Basque
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Catalan
- Cebuano
- China
- China (Taiwan)
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Czech
- Danish
- Dutch
- English
- Esperanto
- Estonian
- Finnish
- French
- Frisian
- Galician
- Georgian
- German
- Greek
- Gujarati
- Haitian Creole
- hausa
- hawaiian
- Hebrew
- Hindi
- Miao
- Hungarian
- Icelandic
- igbo
- Indonesian
- irish
- Italian
- Japanese
- Javanese
- Kannada
- kazakh
- Khmer
- Rwandese
- Korean
- Kurdish
- Kyrgyz
- Lao
- Latin
- Latvian
- Lithuanian
- Luxembourgish
- Macedonian
- Malgashi
- Malay
- Malayalam
- Maltese
- Maori
- Marathi
- Mongolian
- Myanmar
- Nepali
- Norwegian
- Norwegian
- Occitan
- Pashto
- Persian
- Polish
- Portuguese
- Punjabi
- Romanian
- Russian
- Samoan
- Scottish Gaelic
- Serbian
- Sesotho
- Shona
- Sindhi
- Sinhala
- Slovak
- Slovenian
- Somali
- Spanish
- Sundanese
- Swahili
- Swedish
- Tagalog
- Tajik
- Tamil
- Tatar
- Telugu
- Thai
- Turkish
- Turkmen
- Ukrainian
- Urdu
- Uighur
- Uzbek
- Vietnamese
- Welsh
- Bantu
- Yiddish
- Yoruba
- Zulu
டிசம்பர் . 01, 2024 23:19 Back to list
Is Aspartame Safe for Consumption in Everyday Diets and Beverages?
Is Aspartame Safe? A Comprehensive Overview
Aspartame, a low-calorie artificial sweetener, has been the subject of debate since it was first approved for use in food products. Commonly found in a variety of sugar-free and diet products, including beverages, chewing gum, and desserts, aspartame is about 200 times sweeter than sugar. This quality makes it a popular choice for those looking to reduce caloric intake without sacrificing sweetness. However, concerns regarding its safety have persisted over the years, leading to extensive research and regulatory reviews.
The Science Behind Aspartame
Aspartame is made up of two amino acids phenylalanine and aspartic acid, along with a small amount of methanol. Upon ingestion, it is broken down into its constituent parts, which are naturally occurring substances in many foods. These components can be found in everyday items, such as meats, dairy products, and fruits. The FDA approved aspartame for use in food products in 1981, and since then, it has been subjected to rigorous safety assessments.
Several international health organizations, including the World Health Organization (WHO) and the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA), have deemed aspartame safe for human consumption. The acceptable daily intake (ADI) established by these organizations is significantly higher than the amount one would typically consume. For adults, the ADI is set at 40 mg per kilogram of body weight in the EU and 50 mg in the US. This means that an average adult would have to consume an impractically large amount of aspartame daily to reach harmful levels.
Debunking Myths and Misinformation
The safety of aspartame has been clouded by numerous myths and claims, particularly in relation to health issues such as cancer, neurological disorders, and metabolic diseases. Studies conducted over the past several decades have not provided conclusive evidence supporting these claims. For instance, large-scale studies involving thousands of participants have consistently shown no significant link between aspartame consumption and cancer.
aspartame safe
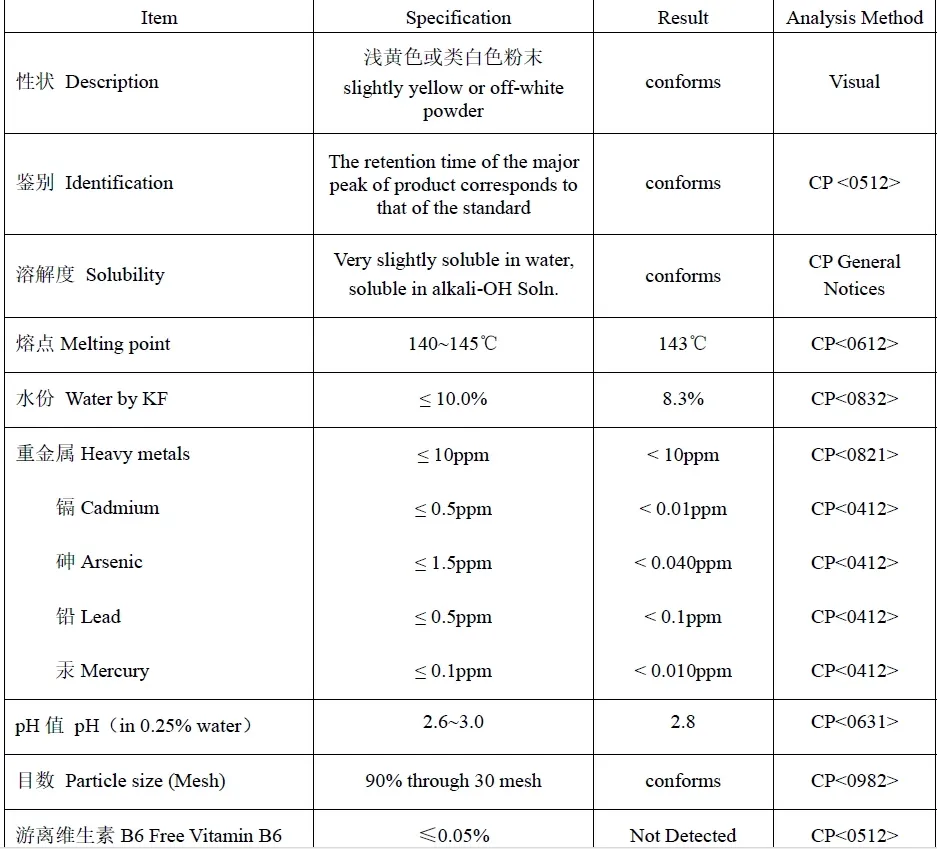
One of the most notable studies included a long-term research project by the Ramazzini Institute, which suggested a potential correlation between aspartame and lymphoma in rats. However, subsequent evaluations by regulatory bodies found the study's methodology flawed and its findings inconclusive. The majority of research conducted under controlled conditions has failed to replicate these outcomes.
For individuals with phenylketonuria (PKU), a rare genetic disorder, aspartame poses risks due to its phenylalanine content. Those affected by PKU must limit their intake of phenylalanine to prevent serious health complications. For the general population, however, aspartame is considered safe.
Benefits and Considerations
One of the primary benefits of aspartame is its ability to provide sweetness without calories, making it an effective tool for weight management and glycemic control. It allows individuals, especially those with diabetes, to enjoy sweet flavors without the associated blood sugar spikes that come from regular sugar consumption. Additionally, it contributes to the overall accessibility of low-calorie and sugar-free products in the market.
However, consumer awareness and personal preferences should guide usage. While scientific evidence supports aspartame's safety, some individuals report sensitivity to it, leading to headaches or gastrointestinal discomfort. As with any food additive, moderation is key.
Conclusion
In conclusion, aspartame continues to be a widely used sweetener supported by extensive research affirming its safety for the majority of the population. Regulatory agencies around the world endorse its use, citing strong evidence that it is safe when consumed within recommended limits. As with all food choices, it's essential to be mindful and informed. For those who choose to include aspartame in their diet, it can be a beneficial alternative to sugar, supporting a range of dietary needs without compromising taste. Whether for weight management, diabetes control, or simply for enjoyment, aspartame proves to be a sweet solution in the world of artificial sweeteners.
Latest news
-
Certifications for Vegetarian and Xanthan Gum Vegetarian
NewsJun.17,2025
-
Sustainability Trends Reshaping the SLES N70 Market
NewsJun.17,2025
-
Propylene Glycol Use in Vaccines: Balancing Function and Perception
NewsJun.17,2025
-
Petroleum Jelly in Skincare: Balancing Benefits and Backlash
NewsJun.17,2025
-
Energy Price Volatility and Ripple Effect on Caprolactam Markets
NewsJun.17,2025
-
Spectroscopic Techniques for Adipic Acid Molecular Weight
NewsJun.17,2025

