Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/www/wwwroot/HTML/www.exportstart.com/wp-content/themes/1198/header.php on line 6
Warning: Undefined array key "file" in /home/www/wwwroot/HTML/www.exportstart.com/wp-content/themes/1198/header.php on line 7
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/www/wwwroot/HTML/www.exportstart.com/wp-content/themes/1198/header.php on line 7
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/www/wwwroot/HTML/www.exportstart.com/wp-content/themes/1198/header.php on line 7
- Afrikaans
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Arabic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Basque
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Catalan
- Cebuano
- China
- China (Taiwan)
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Czech
- Danish
- Dutch
- English
- Esperanto
- Estonian
- Finnish
- French
- Frisian
- Galician
- Georgian
- German
- Greek
- Gujarati
- Haitian Creole
- hausa
- hawaiian
- Hebrew
- Hindi
- Miao
- Hungarian
- Icelandic
- igbo
- Indonesian
- irish
- Italian
- Japanese
- Javanese
- Kannada
- kazakh
- Khmer
- Rwandese
- Korean
- Kurdish
- Kyrgyz
- Lao
- Latin
- Latvian
- Lithuanian
- Luxembourgish
- Macedonian
- Malgashi
- Malay
- Malayalam
- Maltese
- Maori
- Marathi
- Mongolian
- Myanmar
- Nepali
- Norwegian
- Norwegian
- Occitan
- Pashto
- Persian
- Polish
- Portuguese
- Punjabi
- Romanian
- Russian
- Samoan
- Scottish Gaelic
- Serbian
- Sesotho
- Shona
- Sindhi
- Sinhala
- Slovak
- Slovenian
- Somali
- Spanish
- Sundanese
- Swahili
- Swedish
- Tagalog
- Tajik
- Tamil
- Tatar
- Telugu
- Thai
- Turkish
- Turkmen
- Ukrainian
- Urdu
- Uighur
- Uzbek
- Vietnamese
- Welsh
- Bantu
- Yiddish
- Yoruba
- Zulu
Nov . 09, 2024 20:49 Back to list
Innovative Bio-Based Approaches for a Sustainable Future in Adipic Acid Production
The Sustainable Future of Adipic Acid Bio-based Solutions
Adipic acid is a crucial chemical compound, primarily used in the production of nylon, an essential component that plays a pivotal role in various industries, including textiles, automotive, and electronics. Traditionally derived from petroleum, the production of adipic acid raises significant environmental concerns, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions and dependence on fossil fuels. Thus, the quest for sustainable alternatives has become increasingly urgent, leading to the exploration of bio-based solutions for adipic acid production.
The conventional process of manufacturing adipic acid involves the oxidation of cyclohexane, a method that not only consumes a large amount of energy but also emits nitrous oxide, a potent greenhouse gas. In light of the global climate crisis, industries are under pressure to reduce their carbon footprints and incorporate greener production methods. This has paved the way for bio-based adipic acid alternatives derived from renewable resources.
One of the most promising biotechnological approaches to producing adipic acid involves fermentation processes using biomass. Raw materials such as lignocellulosic biomass, glucose, or other carbohydrates from plant sources can be converted into adipic acid through microbial fermentation. These resources are renewable and abundant, which mitigates the dependence on fossil fuels. Researchers are focusing on genetically engineered microorganisms capable of efficiently converting sugars into adipic acid. For example, certain strains of yeast and bacteria have shown promise in high-yield production processes, demonstrating the potential for scalability.
The benefits of bio-based adipic acid extend beyond just the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions. The use of renewable resources contributes to a circular economy, where waste materials can be repurposed into valuable products. For instance, agricultural by-products like corn stover and sugarcane bagasse are not only abundant but often underutilized. Turning these by-products into adipic acid fosters resource efficiency and provides farmers with additional revenue streams.
'sustainable future of adipic acid: bio-based solutions and'
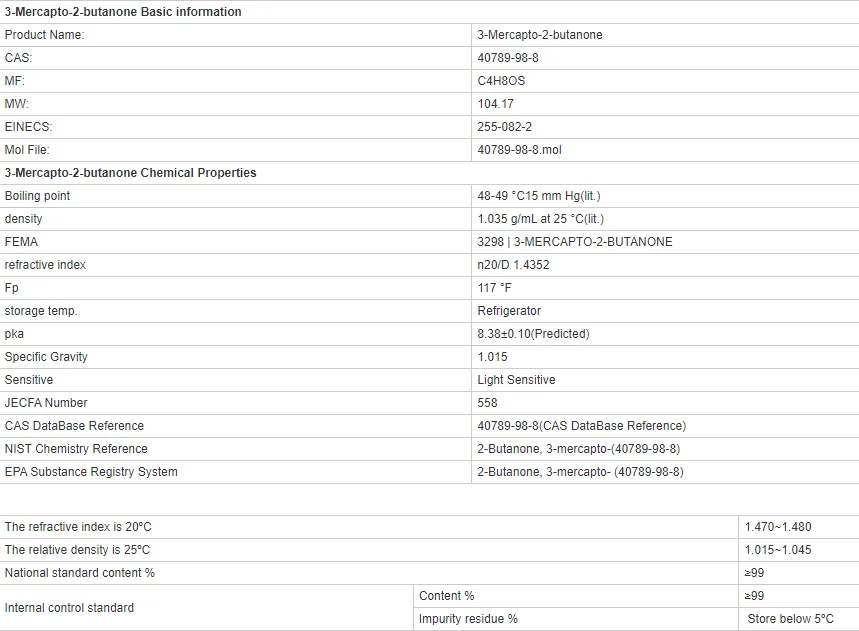
Additionally, bio-based processes often present the opportunity for a more sustainable production spectrum. Traditional petrochemical processes typically require extensive refining and energy inputs, while biotechnological methods may operate at milder conditions, utilizing less energy. This reduction in energy consumption can lead to significant cost savings and environmental benefits across the supply chain.
However, transitioning to bio-based adipic acid production is not without challenges. The initial investment in research and development, infrastructure adaptations, and the need for regulatory approvals can be considerable. Moreover, the scalability of bio-based processes remains a critical concern. While laboratory results are promising, commercial-scale applications require further validation to ensure economic viability.
Moreover, the supply chain also needs to be strengthened to support the complete transition from petrochemical-derived to bio-based adipic acid. This includes establishing reliable sources of raw materials, developing efficient production techniques, and creating markets for bio-based intermediates. Furthermore, consumer awareness and acceptance of bio-based products play a crucial role in driving demand and promoting sustainability.
In conclusion, the sustainable future of adipic acid lies in the successful integration of bio-based solutions into its production. Technologies leveraging renewable resources not only present an opportunity to reduce environmental impact but also foster economic resilience through resource efficiency and circularity. While obstacles remain, the potential benefits far outweigh the challenges. As industries commit to greener practices, bio-based adipic acid production represents a significant step forward in creating a more sustainable chemical industry, contributing to a healthier planet for future generations. The collaboration between scientists, policymakers, and industry stakeholders will be pivotal in navigating this transformative journey towards achieving a sustainable future for adipic acid.
Latest news
-
Certifications for Vegetarian and Xanthan Gum Vegetarian
NewsJun.17,2025
-
Sustainability Trends Reshaping the SLES N70 Market
NewsJun.17,2025
-
Propylene Glycol Use in Vaccines: Balancing Function and Perception
NewsJun.17,2025
-
Petroleum Jelly in Skincare: Balancing Benefits and Backlash
NewsJun.17,2025
-
Energy Price Volatility and Ripple Effect on Caprolactam Markets
NewsJun.17,2025
-
Spectroscopic Techniques for Adipic Acid Molecular Weight
NewsJun.17,2025

