Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/www/wwwroot/HTML/www.exportstart.com/wp-content/themes/1198/header.php on line 6
Warning: Undefined array key "file" in /home/www/wwwroot/HTML/www.exportstart.com/wp-content/themes/1198/header.php on line 7
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/www/wwwroot/HTML/www.exportstart.com/wp-content/themes/1198/header.php on line 7
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/www/wwwroot/HTML/www.exportstart.com/wp-content/themes/1198/header.php on line 7
Hebei Yize Trade Center Co., LTD.!
- Afrikaans
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Arabic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Basque
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Catalan
- Cebuano
- China
- China (Taiwan)
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Czech
- Danish
- Dutch
- English
- Esperanto
- Estonian
- Finnish
- French
- Frisian
- Galician
- Georgian
- German
- Greek
- Gujarati
- Haitian Creole
- hausa
- hawaiian
- Hebrew
- Hindi
- Miao
- Hungarian
- Icelandic
- igbo
- Indonesian
- irish
- Italian
- Japanese
- Javanese
- Kannada
- kazakh
- Khmer
- Rwandese
- Korean
- Kurdish
- Kyrgyz
- Lao
- Latin
- Latvian
- Lithuanian
- Luxembourgish
- Macedonian
- Malgashi
- Malay
- Malayalam
- Maltese
- Maori
- Marathi
- Mongolian
- Myanmar
- Nepali
- Norwegian
- Norwegian
- Occitan
- Pashto
- Persian
- Polish
- Portuguese
- Punjabi
- Romanian
- Russian
- Samoan
- Scottish Gaelic
- Serbian
- Sesotho
- Shona
- Sindhi
- Sinhala
- Slovak
- Slovenian
- Somali
- Spanish
- Sundanese
- Swahili
- Swedish
- Tagalog
- Tajik
- Tamil
- Tatar
- Telugu
- Thai
- Turkish
- Turkmen
- Ukrainian
- Urdu
- Uighur
- Uzbek
- Vietnamese
- Welsh
- Bantu
- Yiddish
- Yoruba
- Zulu
Jan . 17, 2025 01:28 Back to list
monopropylene glycol in food
Monopropylene glycol, commonly referred to as MPG, is fast becoming a focal point in discussions about food safety and ingredient transparency. This versatile chemical compound, a type of glycol, is used across various industries, including food. Highlighting its unique attributes and applications within the food sector can shed light on its role and dispel common misconceptions.
However, consumer perception of chemical ingredients in food can often be clouded by misinformation. It's crucial to address the distinction between monopropylene glycol and ethylene glycol, the latter of which is toxic and not suitable for consumption. Educating consumers about the differences can build trust, as confusion between these substances can lead to unwarranted fear about the safety of food products containing MPG. Real-world experience attests to MPG's reliability and safety. For instance, a major food production company recently launched a line of moisture-sensitive products. By incorporating monopropylene glycol, they achieved not only enhanced shelf life but also customer delight with the product’s consistent quality. This case highlights the role of MPG as not just an ingredient, but as a component integral to fulfilling market demands for quality and safety. In the competitive landscape of food products, companies leveraging monopropylene glycol in innovative ways can stand out. With the push towards clean labels, transparently listing MPG with a clear explanation of its function can serve as a testament to the brand's commitment to quality and consumer education. This practice builds brand authority and enhances trust, as consumers are more likely to support brands that are forthright about their ingredients. In essence, monopropylene glycol is more than just a food additive; it's a multifunctional player that significantly contributes to product excellence. By harnessing its attributes—moisture retention, solubility, safety—companies can ensure product superiority. Moreover, embracing transparency around its use fosters consumer trust and bolsters brand reliability. Addressing consumer concerns and educating the market on its benefits however remains pivotal for its broader acceptance and application in the food industry.

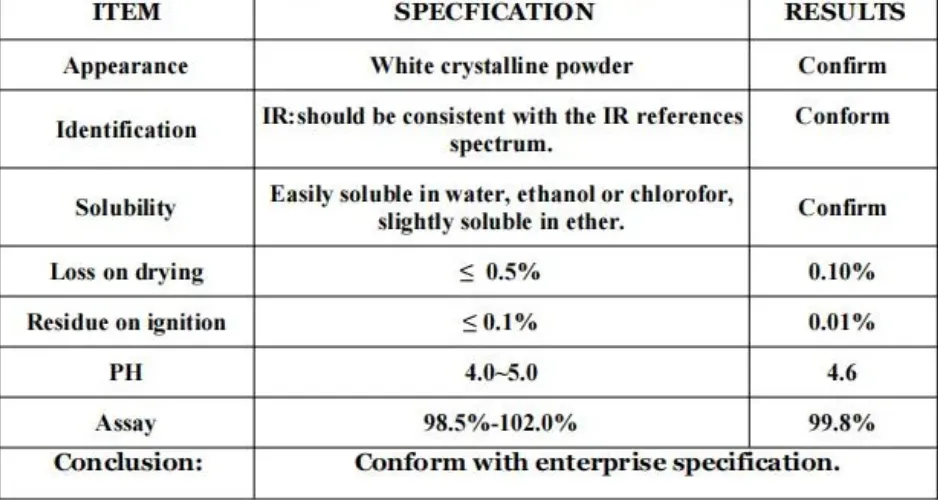
However, consumer perception of chemical ingredients in food can often be clouded by misinformation. It's crucial to address the distinction between monopropylene glycol and ethylene glycol, the latter of which is toxic and not suitable for consumption. Educating consumers about the differences can build trust, as confusion between these substances can lead to unwarranted fear about the safety of food products containing MPG. Real-world experience attests to MPG's reliability and safety. For instance, a major food production company recently launched a line of moisture-sensitive products. By incorporating monopropylene glycol, they achieved not only enhanced shelf life but also customer delight with the product’s consistent quality. This case highlights the role of MPG as not just an ingredient, but as a component integral to fulfilling market demands for quality and safety. In the competitive landscape of food products, companies leveraging monopropylene glycol in innovative ways can stand out. With the push towards clean labels, transparently listing MPG with a clear explanation of its function can serve as a testament to the brand's commitment to quality and consumer education. This practice builds brand authority and enhances trust, as consumers are more likely to support brands that are forthright about their ingredients. In essence, monopropylene glycol is more than just a food additive; it's a multifunctional player that significantly contributes to product excellence. By harnessing its attributes—moisture retention, solubility, safety—companies can ensure product superiority. Moreover, embracing transparency around its use fosters consumer trust and bolsters brand reliability. Addressing consumer concerns and educating the market on its benefits however remains pivotal for its broader acceptance and application in the food industry.
Latest news
-
Certifications for Vegetarian and Xanthan Gum Vegetarian
NewsJun.17,2025
-
Sustainability Trends Reshaping the SLES N70 Market
NewsJun.17,2025
-
Propylene Glycol Use in Vaccines: Balancing Function and Perception
NewsJun.17,2025
-
Petroleum Jelly in Skincare: Balancing Benefits and Backlash
NewsJun.17,2025
-
Energy Price Volatility and Ripple Effect on Caprolactam Markets
NewsJun.17,2025
-
Spectroscopic Techniques for Adipic Acid Molecular Weight
NewsJun.17,2025

