Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/www/wwwroot/HTML/www.exportstart.com/wp-content/themes/1198/header.php on line 6
Warning: Undefined array key "file" in /home/www/wwwroot/HTML/www.exportstart.com/wp-content/themes/1198/header.php on line 7
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/www/wwwroot/HTML/www.exportstart.com/wp-content/themes/1198/header.php on line 7
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/www/wwwroot/HTML/www.exportstart.com/wp-content/themes/1198/header.php on line 7
- Afrikaans
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Arabic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Basque
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Catalan
- Cebuano
- China
- China (Taiwan)
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Czech
- Danish
- Dutch
- English
- Esperanto
- Estonian
- Finnish
- French
- Frisian
- Galician
- Georgian
- German
- Greek
- Gujarati
- Haitian Creole
- hausa
- hawaiian
- Hebrew
- Hindi
- Miao
- Hungarian
- Icelandic
- igbo
- Indonesian
- irish
- Italian
- Japanese
- Javanese
- Kannada
- kazakh
- Khmer
- Rwandese
- Korean
- Kurdish
- Kyrgyz
- Lao
- Latin
- Latvian
- Lithuanian
- Luxembourgish
- Macedonian
- Malgashi
- Malay
- Malayalam
- Maltese
- Maori
- Marathi
- Mongolian
- Myanmar
- Nepali
- Norwegian
- Norwegian
- Occitan
- Pashto
- Persian
- Polish
- Portuguese
- Punjabi
- Romanian
- Russian
- Samoan
- Scottish Gaelic
- Serbian
- Sesotho
- Shona
- Sindhi
- Sinhala
- Slovak
- Slovenian
- Somali
- Spanish
- Sundanese
- Swahili
- Swedish
- Tagalog
- Tajik
- Tamil
- Tatar
- Telugu
- Thai
- Turkish
- Turkmen
- Ukrainian
- Urdu
- Uighur
- Uzbek
- Vietnamese
- Welsh
- Bantu
- Yiddish
- Yoruba
- Zulu
Lis . 10, 2024 11:16 Back to list
Exploring the Benefits and Risks of Aspartame and Acesulfame K in Food Products
Understanding Aspartame and Acesulfame K Sweeteners Under Scrutiny
In the world of food and beverage production, the use of artificial sweeteners has surged over the past few decades as consumers increasingly seek healthier alternatives to sugar. Among these sweeteners, aspartame and acesulfame potassium (often abbreviated as acesulfame K) are two of the most prominent. Both are utilized extensively in a variety of products, from diet sodas to sugar-free desserts. While they promise low-calorie sweetness, their safety and health implications have drawn considerable scrutiny and debate.
What are Aspartame and Acesulfame K?
Aspartame is a low-calorie artificial sweetener composed of two amino acids—phenylalanine and aspartic acid—along with a methanol group. It is approximately 200 times sweeter than sucrose (table sugar), allowing it to be used in minimal quantities to achieve the desired sweetness. Acesulfame K, on the other hand, is a potassium salt that is also significantly sweeter than sugar, offering about 200 times the sweetness per gram. It is often used in combination with other sweeteners to enhance flavor profiles and mask any bitter aftertastes.
Applications in Food and Beverage
These sweeteners have found their place in a myriad of products. Aspartame is frequently found in diet sodas, sugar-free chewing gum, and various low-calorie food items. Acesulfame K is common in similar products and is often employed in baking because it remains stable under heat—a significant advantage over other sweeteners. Their ability to provide sweetness without extra calories has made them particularly attractive for weight management and diabetic-friendly products.
Safety and Health Concerns
aspartame y acesulfame k
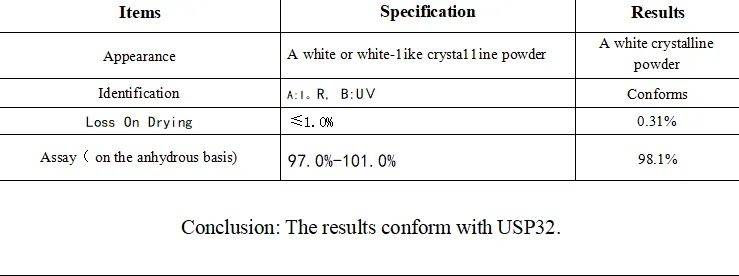
Despite their widespread use, both aspartame and acesulfame K have come under fire regarding their safety. The most notable concern surrounding aspartame relates to its breakdown products, particularly phenylalanine, which can pose a risk to individuals with the genetic disorder phenylketonuria (PKU). Excessive consumption has also been linked to potential headaches, allergic reactions, and other health issues, although numerous studies and health organizations, including the FDA, have deemed aspartame safe for general consumption when used within established daily intake levels.
Acesulfame K, similarly, faces scrutiny. Studies have raised questions about its long-term health effects, potential cancer risks, and its impact on metabolism. Regulatory bodies, including the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) and the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), have reviewed the existing data and set acceptable daily intake levels. Nevertheless, consumer skepticism persists, fueled in part by internet theories and anecdotal claims suggesting the sweeteners could have adverse health effects.
The Consumer Perspective
As consumers become more educated about their food choices, many are opting for natural sweeteners like stevia and honey, leaving artificial options like aspartame and acesulfame K in a precarious position. Labeling initiatives also contribute to this shift, with many brands opting to highlight natural ingredients, which often leads to the exclusion of artificial sweeteners. Nevertheless, the convenience, shelf stability, and cost-effectiveness of aspartame and acesulfame K mean they remain a staple in many food products.
Conclusion
In summary, both aspartame and acesulfame K serve essential roles in the modern food industry, providing sweetness without the calories associated with sugar. However, ongoing debates about their safety continue to shape consumer choices and regulatory policies. As research evolves and more information becomes available, it is crucial for consumers to stay informed and consult scientific guidance when making dietary decisions. While moderation remains key, the ultimate choice between artificial sweeteners and natural alternatives often boils down to personal preference, health goals, and perceptions of safety.
Latest news
-
Certifications for Vegetarian and Xanthan Gum Vegetarian
NewsJun.17,2025
-
Sustainability Trends Reshaping the SLES N70 Market
NewsJun.17,2025
-
Propylene Glycol Use in Vaccines: Balancing Function and Perception
NewsJun.17,2025
-
Petroleum Jelly in Skincare: Balancing Benefits and Backlash
NewsJun.17,2025
-
Energy Price Volatility and Ripple Effect on Caprolactam Markets
NewsJun.17,2025
-
Spectroscopic Techniques for Adipic Acid Molecular Weight
NewsJun.17,2025

